What is Photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria make their own food using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. It is one of the most important biological processes on Earth because it produces oxygen and provides energy for nearly all living things.
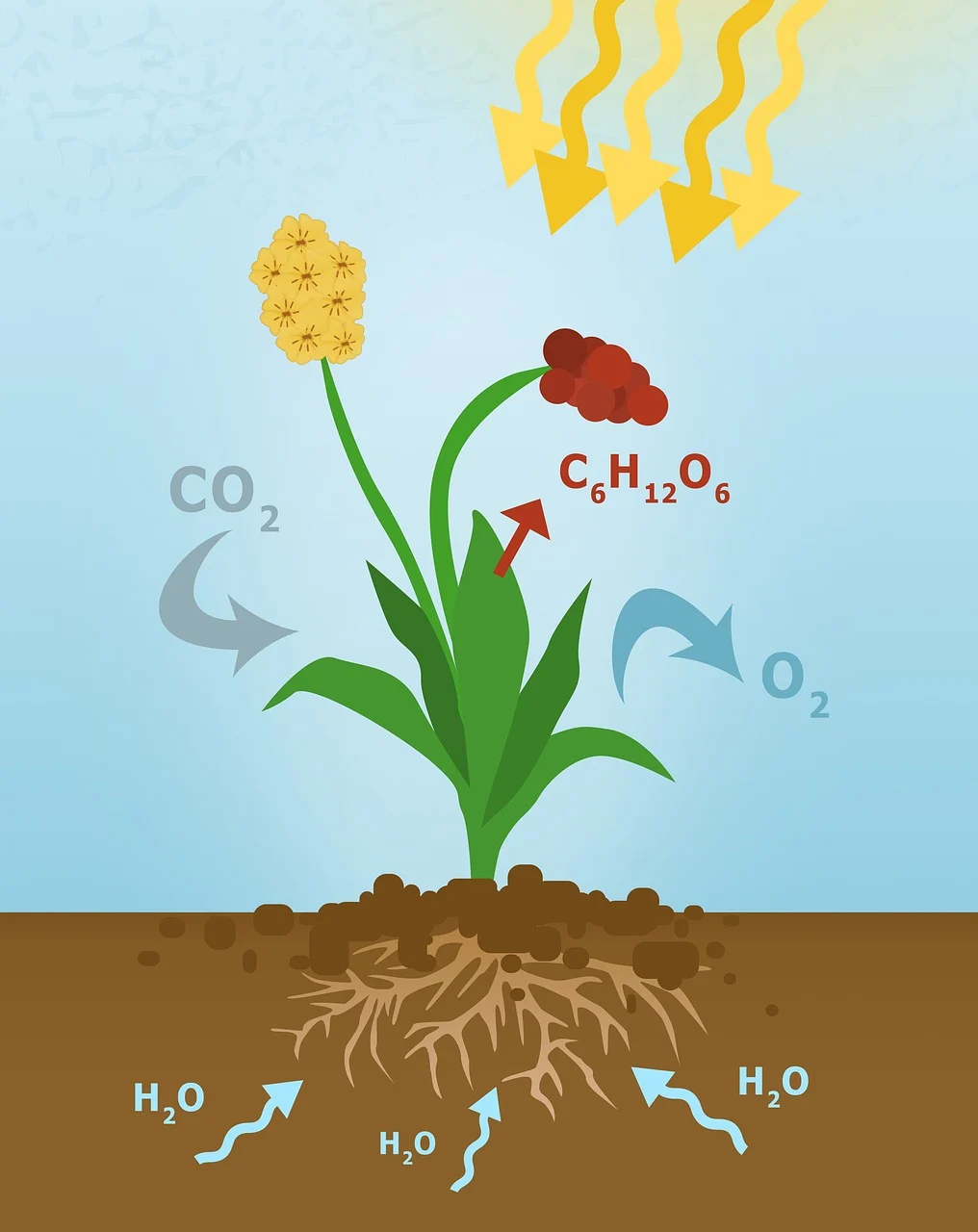
The Basic Equation
Photosynthesis can be summarized in a simple chemical equation:
Carbon Dioxide + Water + Sunlight → Glucose + Oxygen
In scientific terms:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + light energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
This means that six molecules of carbon dioxide and six molecules of water, with the help of light energy, produce one molecule of glucose (a type of sugar) and six molecules of oxygen.
Where Does Photosynthesis Happen?
Photosynthesis mainly occurs in the leaves of plants. Inside the leaf cells are tiny structures called chloroplasts, which contain a green pigment called chlorophyll. This pigment is responsible for capturing sunlight and giving plants their green color.
The Two Stages of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis happens in two main stages:
- Light-dependent reactions: These occur in the presence of sunlight. Chlorophyll absorbs the light energy, which is then used to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. The oxygen is released into the air.
- Light-independent reactions (Calvin Cycle): These don’t need sunlight directly. The plant uses carbon dioxide and the energy produced in the first stage to create glucose, which the plant stores and uses for energy.
Why is Photosynthesis Important?
Photosynthesis is essential for life on Earth for several reasons:
- It produces oxygen: The oxygen we breathe comes from the process of photosynthesis.
- It provides food: Plants make their own food and also serve as food for animals and humans.
- It supports ecosystems: All food chains begin with plants or algae that photosynthesize.
- It helps reduce carbon dioxide: Plants absorb carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, from the atmosphere.
Interesting Facts
- Only green parts of a plant carry out photosynthesis.
- Without photosynthesis, life on Earth as we know it wouldn’t exist.
- Algae in oceans produce more oxygen than all the forests on Earth combined.
Conclusion: Photosynthesis is nature’s way of powering life on Earth. It not only feeds the plant itself but also supplies energy and oxygen to other organisms. Understanding photosynthesis helps us appreciate the role plants play in maintaining a healthy and balanced planet.